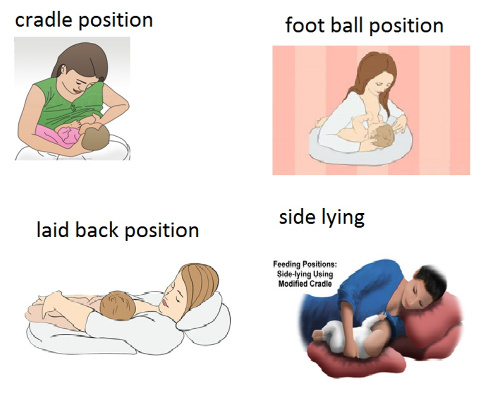
Breast feeding positioning
Learn how to be a breast feeding pro with these easy positions!
Short-term benefits for the baby:
- Breastfeeding reduces the risk of illness due to contaminated water, which under some conditions can occur with formula.
- Breast milk is a source of lactose and essential fatty acids that help a baby’s brain grow and develop.
- Breast milk helps regulate healthy bacteria in the baby’s gut.
- Breastfed babies have fewer cases of ear infections, gastrointestinal infections, bacterial meningitis, urinary tract infections, late-onset sepsis in pre-term babies, and more.
- Colostrums—the first milk produced at birth—contains high amounts of carbohydrates, protein and antibodies, and it has yet to be replicated as formula.
- Breast milk works as an antibiotic against E. coli and staphylococci, among others.
Long-term benefits for the baby:
- Breastfeeding as an infant can lead to higher IQ, especially if breastfed exclusively and for a longer period of time.
- Babies who are breastfed have a lower risk of obesity later in life.
- Children and adults who were breastfed have a lower rate of food allergies, asthma, eczema, Celiac Disease, and Type I and Type II diabetes, among others.
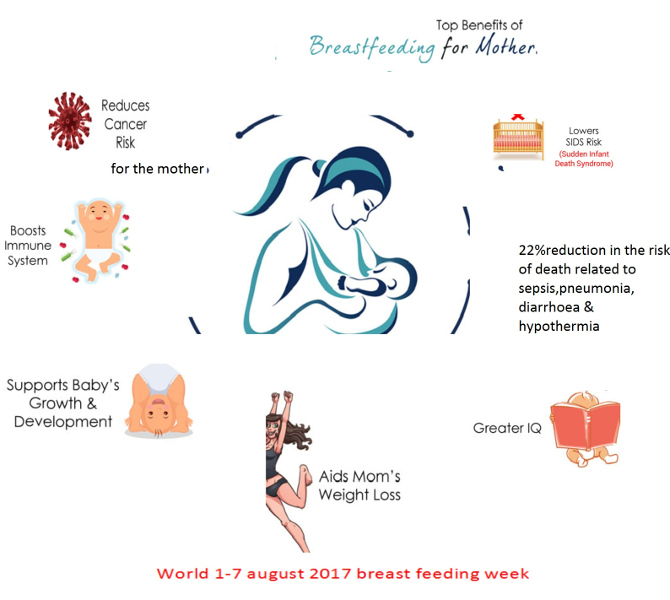
Short-term benefits for the mother:
- Breastfeeding releases the “love” hormone oxytocin in the mother, which improves the bonding between mother and baby.
- The release of oxytocin after birth also aids in contracting the uterus to prevent postpartum hemorrhage and to reduce the uterus to pre-pregnancy size.
- Women have a decreased risk of iron-deficiency anemia while nursing.
- Fertility and chance of becoming pregnant is greatly reduced in the first six months of exclusive breastfeeding, aiding in family planning.
- Milk production helps with post-partum weight loss.
Long-term benefits for the mother:
- Moms who breastfeed have lower rates of ovarian, breast and endometrial cancer.
- Women who breastfed may have higher bone density and lower rates of osteoporosis later in life.
Foods to avoid during breast feeding:
- Chocolate
- Spices (cinnamon, garlic, curry, chili pepper)
- Citrus fruits and their juices, like oranges, lemons, limes, and grapefruit
- Strawberries
- Kiwifruit
- Pineapple
- The “gassy” veggies (onion, cabbage, garlic, cauliflower, broccoli, cucumbers, and peppers)
- Fruits with a laxative effect, such as cherries and prunes
How long to breast feed your baby?
Breast milk is recommended for about the first six months (26 weeks) of your baby’s life.
Healthy tips:
- Drink water, milk and fruit juices as needed.
- You need to eat more than usual to replenish energy that is lost through breastfeeding.
- Energy is essential, so eat regularly to increase your food intake and meet all your nutritional needs.
- Keep your intake of empty calorie foods to the minimum and eat more nutrient-dense foods.
- Plan your meals well and use the food pyramid as a guide in selecting your daily foods. Include plenty of fresh fruit, vegetables, milk and milk products, fish, poultry, nuts, whole grains, parboiled rice, beans and lentils.